3.6V C ER26500 Li-SoCl2 Battery (8500/9000mAh) | Pkcell
Understanding ER26500 Battery
The ER26500 battery is a primary lithium battery. This means you can not recharge it. It uses lithium-thionyl chloride (Li-SOCl₂) as its chemical makeup and has a cylinder shape. This battery operates at a voltage of 3.6V. The name "ER26500" refers to its size, which is 26.2mm in diameter and 50.5mm in height. It is classified as a 'C' size battery. The ER26500 size C 3.6 V batteries are great for devices that run on a higher voltage. Their strong voltage and good discharge features make them a top choice for many purposes. These batteries are made for devices that require lasting, steady power, such as water meters, GPS trackers, industrial sensors, and security systems.
Key Features of Pkcell ER26500
- High and Stable Voltage
- High Minimum Voltage During Pulsing
- Stainless Steel Container
- Hermetic Glass-to-metal Sealing
- Low Self-discharge Rate (Less than 1% After 1 year of Storage at +25℃)
- Wide Operating Temperature (-60℃~+85℃)
- Restricted for transport(class 9)
Main Applications of Pkcell ER26500
- Gas Metering
- Utility Metering
- Alarms and Security Devices
- Memory Back-up
- Tracking Systems
- Professional Electronics
Case study - PKCELL Lithium Batteries Ensure Long-Term Reliability for Canadian Smart Parking Sensors
A Canadian company specializing in the development of smart parking sensor systems for intelligent transportation and smart city applications required a highly dependable power solution for its outdoor devices. PKCELL recommended a suite of Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries to meet the diverse power needs of the customer's parking sensor system. Finally, the client decided to use our 3.6V 18000mah ER26500+HPC1520 battery pack and the successful test results have led the customer to plan for a long-term supply partnership and increase annual purchase quantities.
Learn more details here: PKCELL LiSoCl2 Battery: Reliable for Smart Parking Sensors
Cost-effective Alternatives to Tadiran, Saft, Xeno & Tekcell
| PKCELL ER Model | Equivalent Competitor Model(s) |
|---|---|
| ER26500 | LS26500 (Saft) |
| ER14505 | LS14500 (Saft), XL-145F (Xeno), Tekcell SB-AA02, TL-5186 (varies) |
| ER14250 | TL-5902 (Tadiran), Tekcell 1/2AA, TL-2150, XL-060F, XL-055F, SL-760, TL-5104, LS14250 |
| ER17505 | LS17500 (Saft) |
| ER34615 | LS33600 (Saft), TL-5930 (Tadiran), TL-5920, XL-205F, LSH20 (Saft) |
| ER18505 | LS-18505, TL-5955 (Tadiran) |
| ER17335 | LS-17335, TL-5903 (Tadiran), TL-5903S |
Specification Of Other Li-SOCl2(Energy Type) Models
| Model IEC | Nominal Voltage | Dimensions | Nominal Capacity | Standard Current | Max Continuous Discharge Current | Max Pulse Discharge Current | Cut-off Voltage | Weight Approx | Operating Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER10450 | AAA | 3.6 | 10.0×45.0 | 800 | 1.00 | 50 | 60 | 2.00 | 9 | -55~+85 |
| ER14250 | 1/2AA | 3.6 | 14.5×25.0 | 1200 | 0.50 | 20 | 45 | 2.00 | 10 | -55~+85 |
| ER14335 | 2/3AA | 3.6 | 14.5×33.5 | 1650 | 0.70 | 75 | 150 | 2.00 | 13 | -55~+85 |
| ER14505 | AA | 3.6 | 14.5×50.5 | 2400 | 1.00 | 100 | 200 | 2.00 | 19 | -55~+85 |
| ER17335 | 3.6 | 17×33.5 | 2100 | 1.00 | 100 | 200 | 2.00 | 30 | -55~+85 | |
| ER17505 | 3.6 | 17×50.5 | 3400 | 1.00 | 100 | 200 | 2.00 | 32 | -55~+85 | |
| ER18505 | A | 3.6 | 18.5×50.5 | 4000 | 1.00 | 120 | 200 | 2.00 | 32 | -55~+85 |
| ER26500 | C | 3.6 | 26.2×50.5 | 8500 | 2.00 | 130 | 300 | 2.00 | 55 | -55~+85 |
| ER34615 | D | 3.6 | 34.2×61.5 | 19000 | 3.00 | 200 | 400 | 2.00 | 107 | -55~+85 |
| ER9V | 3.6 | 48.8×17.8×7.5 | 8500 | 2.00 | 130 | 300 | 2.00 | 16 | -55~+85 | |
More Than Just Individual Cells - We Offer Complete Power Solutions.
- Single Battery With Cables and Connectors
- Custom LiSOCl2 Battery Packs Based on Your Tailored Needs
Why Choose Pkcell Battery?
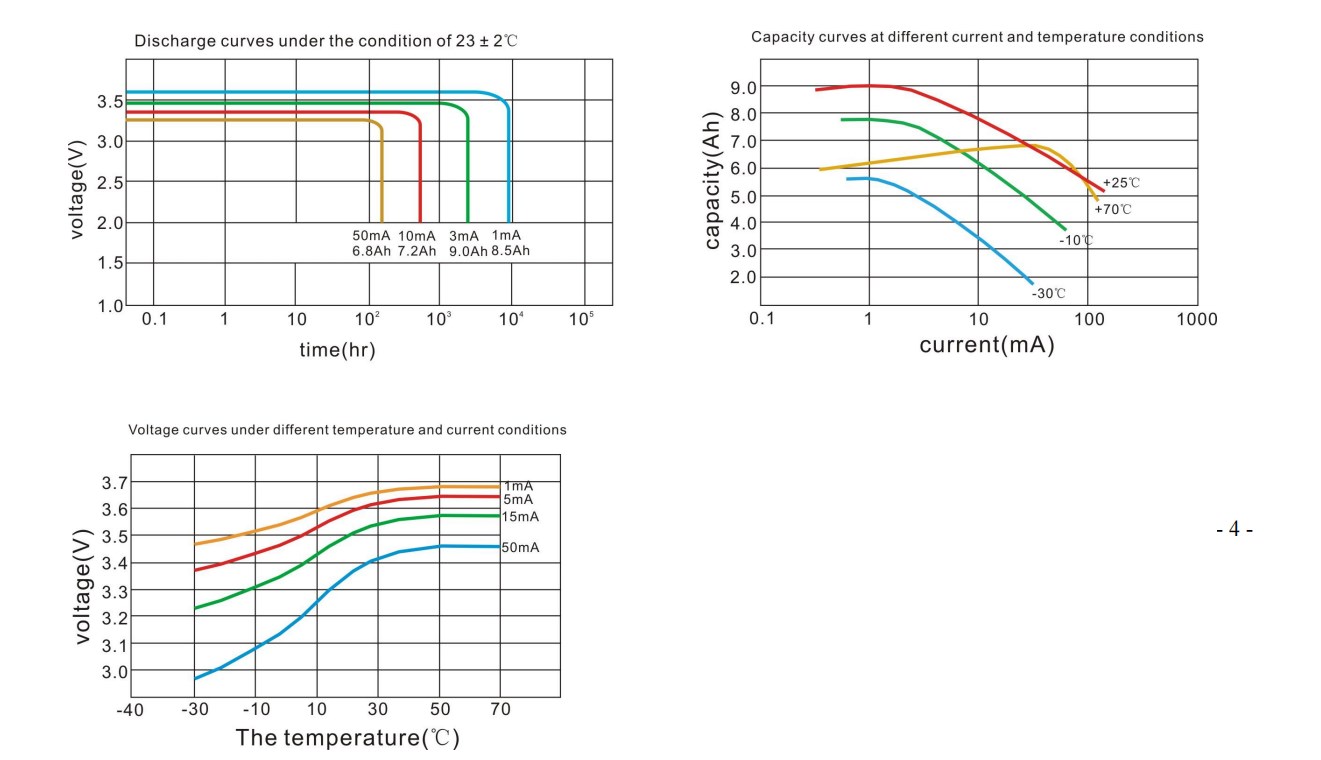
Typical Discharge Characteristics
Warning:
- These are non rechargeable batteries.
- Do not recharge, short circuit,crush, disassemble, heat above 100℃ incinerate.
- Do not use the battery beyond the permitted temperature range.
Frequently Asked About LiSoCl2 Battery
- Lead Time: Standard samples typically arrive in 7-12 days. Formal orders usually take around 25 days, though smaller quantities might ship faster, potentially within 15-18 days.
- Payment Methods: We accept various payment types, including T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and PayPal.
- Shipping: We offer flexibility! Depending on your needs and location, we can ship your order via air freight (using carriers like FEDEX, DHL, UPS, EMS, etc.) or via sea freight.
- Delivery Terms: We can work with several common international shipping terms, including EXW, FCA, FOB, CFR, and DDU.
We have a minimum order value of USD $500. The actual quantity you receive depends on the unit price of the specific batteries you choose. Absolutely! We understand you need to test our products. We're happy to provide samples for your evaluation before you place a formal order.
Passivation is an interesting natural phenomenon observed in Lithium Thionyl Chloride (LiSO₂Cl₂) batteries! When lithium metal touches the thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) electrolyte, a thin, protective layer forms on the surface of the lithium negative electrode. This layer, mostly made up of Lithium Chloride (LiCl), creates a high-resistance barrier that prevents a continuous reaction between the lithium and the electrolyte. Isn't it fascinating how this process helps maintain the battery's performance?
Passivation has some excellent benefits along with a few potential drawbacks that are important to consider:
Benefits:
- Low Self-Discharge: The passivation layer does a fantastic job of slowing down any unwanted side reactions between the lithium and the electrolyte, leading to an impressively low self-discharge rate. Thanks to this, LiSO₂Cl₂ batteries can be stored for many years, often over 10 years, while still keeping most of their capacity intact.
- Long Shelf Life: Because of the low self-discharge, these batteries can hold onto their energy for quite an extended period, which is great for long-term storage.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Voltage Delay: When a passivated battery starts discharging—especially after being stored or during high-current pulses—the current first needs to break through or dissolve the high-resistance passivation layer. This can temporarily drop the battery's voltage below its normal operating level before it bounces back. This occurrence is often referred to as "voltage delay."
It uses Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl₂) chemistry, which offers high energy density, wide operating temperature (-55°C to +85°C), and excellent shelf life of up to 10–15 years.
Depending on the application, the ER26500 battery can last up to 10 years or more, especially in low-drain devices or when paired with a capacitor or hybrid pulse capacitor (HPC) for handling pulses.
No. The ER26500 is a primary lithium battery and is not rechargeable. Attempting to recharge it may cause dangerous reactions.
Although they share the same size, ER26500 offers much higher energy capacity, longer life, and more stable performance under extreme conditions compared to alkaline or NiMH C batteries.
Yes. ER26500 is available with various terminations like tabs, wires, or connectors, and can be used individually or in battery packs designed for specific industrial and OEM applications.















